Masonic, Occult and Esoteric Online Library
The Egyptian Book of the Dead
By E. A. Wallis Budge
Plate III.
Vignette: Scene of the weighing of the Heart of the Dead. Ani and his wife enter the Hall of Double Law or Truth, wherein the heart, emblematical of the conscience, is to be weighed in the balance against the feather, emblematical of law. Above, twelve gods, each holding a sceptre are seated upon thrones before a table of offerings of fruit, flowers, etc. Their names are: Harmachis, "the great god within his boat"; Tmu; Shu; Tefnut, "lady of heaven"; Seb; Nut, "lady of Heaven" Isis; Nephthys; Horus, "the great god"; Hathor, "lady of Amenta"; and Sa. Upon the beam of the scales sits the dog-headed ape which was associated
[1. A name of the underworld.
2. Or Sexet-Anru, a division of the Sexet-hetepu (see Plate XXXV.), the Elysian fields wherein the souls of the blessed were supposed to reap and sow.
3. In British Museum papyrus No. 9901 the goddess Maat is seated on the centre of the beam of the balance. The double Maat goddesses are at times represented standing beside the balance to watch the result of the weighing, and at the same time Maat is also placed in the scale to be weighed against the heart of the deceased (Fig. x) (see Naville, Todtenbuch, Bd. I., Bl. 136, Pa.). {footnote page 256} In the papyrus of Qenna the head of Anubis is on the beam, and the ape, wearing disk and crescent, is seated upon a pylon-shaped pedestal beside the balance (Fig. 2). Another vignette shows Horus holding Maat in his band, weighing the heart in the presence of the Maat goddesses, and Anubis, holding the deceased by the hand, presents the heart to Osiris while Isis and Nephthys in the form of apes sit near (Fig. 3).
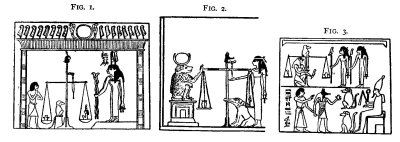 with Thoth,[1] the scribe of the gods. The god Anubis, jackal-headed, tests the tongue of the balance, the suspending bracket of which is in the form of the feather The inscription above the head of Anubis reads:--"He who is in the tomb saith, pray thee, O weigher of righteousness, to guide (?) the balance that it may be stablished.'" On the left of the balance, facing Anubis, stands Ani's "Luck" or "Destiny," Shai and above is the object called mesxen which has been described[2] as "a cubit with human head," and which is supposed to be connected with the place of birth. Behind these stand the goddesses Meskhenet and Renenet: Meskhenet[3]
with Thoth,[1] the scribe of the gods. The god Anubis, jackal-headed, tests the tongue of the balance, the suspending bracket of which is in the form of the feather The inscription above the head of Anubis reads:--"He who is in the tomb saith, pray thee, O weigher of righteousness, to guide (?) the balance that it may be stablished.'" On the left of the balance, facing Anubis, stands Ani's "Luck" or "Destiny," Shai and above is the object called mesxen which has been described[2] as "a cubit with human head," and which is supposed to be connected with the place of birth. Behind these stand the goddesses Meskhenet and Renenet: Meskhenet[3]
[1. In the papyrus of Sutimes (Naville, Todtenbuch, Bd. I., Bl. 43) the ape is called neb xemennu ut a maa, "Lord of Khemennu, just weigher"; and in British Museum papyrus No. 9900, "Thoth, lord of the scales."
2. Birch, in Bunsen's Egypt's Place, vol. v., p. 259. In the papyrus of Anhai (British Museum, No. 10,472) there is a meskhen on each side of the upright of the balance: one is called Shai and the other Renen.
3. Four goddesses bore the name of Meskhen, and they were supposed to assist the resurrection of Osiris; they were associated with Tefnut, Nut, Isis, and Nephthys (see Lepsius, Denkmäler, iv., Bl. 59a; and Mariette, Dendérah, iv., pl. 74 a). Each wore upon her head the object ###, which is said by some to represent the blossoms of palm trees (Lanzone, Dizionario, p. 329). Examples of this as an amulet, in hard stone, in the British Museum, are Nos. 8158, 8159, 8161, 20,618, and, in porcelain, No. 15,963.]
presiding over the birth-chamber, and Renenet[1] probably superintending the rearing of children. Behind the meskhen is the soul of Ani in the form of a human-headed bird standing on a pylon. On the right of the balance, behind Anubis, stands Thoth,[2] the scribe of the gods, with his reed-pen and palette[3] containing black and red ink, with which to record the result of the trial. Behind Thoth stands the female monster Amam[4], the "Devourer," or Am-mit, the eater of the Dead."
[1. The name of this goddess is probably connected with the word renen, "to suckle." M. Pierret identifies her with the goddess of that name who presided over harvests, and is described as the "lady of the offerings of all the gods" (Panthéon, p. 61), having a snake's head, which in some instances is surmounted by the disk, horns and feathers of the goddess Hathor (see Lanzone, Dizionario, tav. 188, No. 2).
2 Thoth was the personification of intelligence. He was self-created and self-existent, and was the "heart of Ra." He invented writing, letters, the arts and sciences, and he was skilled in astronomy and mathematics. Among his many titles are "lord of Law," "maker of Law," and "begetter of Law." He justified Osiris against his enemies, and he wrote the story of the fight between Horus, the son of Osiris, and Set. As "lord of Law" he presides over the trial of the heart of the dead, and, as being the justifier of the god Osiris against his enemies, he is represented in funereal scenes as the justifier also of the dead before Osiris (see Lanzone, Dizionario, p. 1264 ff., and tav. cccciv., No. i; Pierret, Panthéon, pp. 10-14; and Brugsch, Religion und Mythologie, p. 439 ff.). Brugsch connects the name Tehuti (Thoth) with the old Egyptian word tehu, "ibis," and he believes that it means the "being who is like an ibis." The word tex also means "to measure," "to compute," "to weigh"; and as this god is called "the counter of the heavens and the stars, and of all that therein is," the connexion of the name Thoth with tex is evident. Bronze and faïence figures of the god represent him with the head of an ibis, and holding an utchat in his hands (see Nos. 481, 490a, and 11,385 in the British Museum). The utchat, or eye of the sun, has reference to the belief that Thoth brought back each morning the light of the sun which had been removed during the night.
3. The palettes of the Egyptian scribe were rectangular, and were made of wood, stone, basalt, ivory (see Nos. 5512a, 5513, 5525a, and 12,779, etc., in the British Museum). They measure from 10 to 17 inches in length, and from 2 to 3 inches in width. They usually contain two round cavities to hold red and black ink, and a groove to hold the reed-pens. The inscriptions on them, which usually have reference to Thoth, are cut, or written in ink, or inlaid in colour; the name of the owner of the palette is generally added. The colours with which the Egyptians wrote were made of vegetable substances, coloured earths, and preparations of copper.
4 She is also called "Devourer of Amenta" (i.e., the underworld), and Shai (see Lanzone, Dizionario, p. 129). In the British Museum papyrus No. 9901 she is described as hat en emsuh; pehu-s em tebt her-ab-set em ma "the fore-part of a crocodile; her hind-quarters are those of a hippopotamus; her middle part [is that] of a lion."
{footnote p. 258} The Devourer usually stands near the balance instead of behind Thoth; but there is one papyrus quoted by Naville, (Todtenbuch, Bd. I., Bl. 136) in which she is shown crouching beside the lake of fire in the infernal regions.
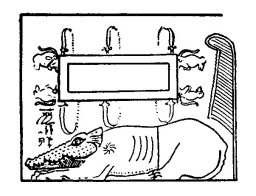 Text: [Chapter XXXB.] Osiris, the scribe Ani, saith:[1] "My heart my mother, my heart my mother, my heart my coming into being! May there be nothing to resist me at [my] judgment; may there be no opposition to me from the Tchatcha;[2] may there be no parting of thee from me in the presence of him who keepeth the scales! Thou art my ka within my body [which] knitteth[3] and strengtheneth my limbs. Mayest thou come forth to the place of happiness to which[4] I am advancing. "May the Shenit[5] not cause my name to stink, and may no lies be spoken against me in the presence of the god![6] Good is it for thee to hear."[7] . . . . . . .
Text: [Chapter XXXB.] Osiris, the scribe Ani, saith:[1] "My heart my mother, my heart my mother, my heart my coming into being! May there be nothing to resist me at [my] judgment; may there be no opposition to me from the Tchatcha;[2] may there be no parting of thee from me in the presence of him who keepeth the scales! Thou art my ka within my body [which] knitteth[3] and strengtheneth my limbs. Mayest thou come forth to the place of happiness to which[4] I am advancing. "May the Shenit[5] not cause my name to stink, and may no lies be spoken against me in the presence of the god![6] Good is it for thee to hear."[7] . . . . . . .
Thoth, the righteous judge of the great company of the gods who are in the presence of the god Osiris, saith: "Hear ye this judgment. The heart of Osiris hath in very truth been weighed, and his soul hath stood as a witness for him; it hath been found true by trial in the Great Balance. There hath not been found any wickedness in him; he hath not wasted the offerings in the temples; he hath not done harm by his deeds; and he uttered no evil reports while he was upon earth."
The great company of the gods reply to Thoth dwelling in Khemennu: "That which cometh forth from thy mouth hath been ordained. Osiris, the scribe
[1. Ani's speech forms the text of Chapter XXXB. as numbered by M. Naville (Todtenbuch, Bd. I., Bl. 43).
2. The four gods of the cardinal points, Mestha, Hapi, Tuamautef, and Qebhsennuf (see Naville, Todtenbuch Einleitung, p. 164).
Some copies read, "Thou art my ka within my body, the god Khnemu (i.e., "Moulder"), who uniteth (or formeth) and strengtheneth my limbs." Khnemu was called "builder of men, maker of the gods, the father from the beginning; creator of things which are," etc.
4 British Museum papyrus No. 9901 has "place of happiness to which thou goest with me."
5 A class of divine beings.
6 I.e., "the great god, lord of Amenta."
7. This sentence appears to be unfinished; see the Egyptian text, p. 12.]
Ani, triumphant, is holy and righteous. He hath not sinned, neither hath he done evil against us. Let it not be given to the devourer Amemet to prevail over him. Meat-offerings and entrance into the presence of the god Osiris shall be granted unto him, together with a homestead for ever in Sekhet-hetepu, as unto the followers of Horus."